DIFFUSION TENSOR CARDIAC MAGNETIC RESONANCE
Cardiomyocytes are syncytially arranged in differing helically aligned orientations throughout the depth of the myocardial wall and organised into secondary structures called sheetlets.
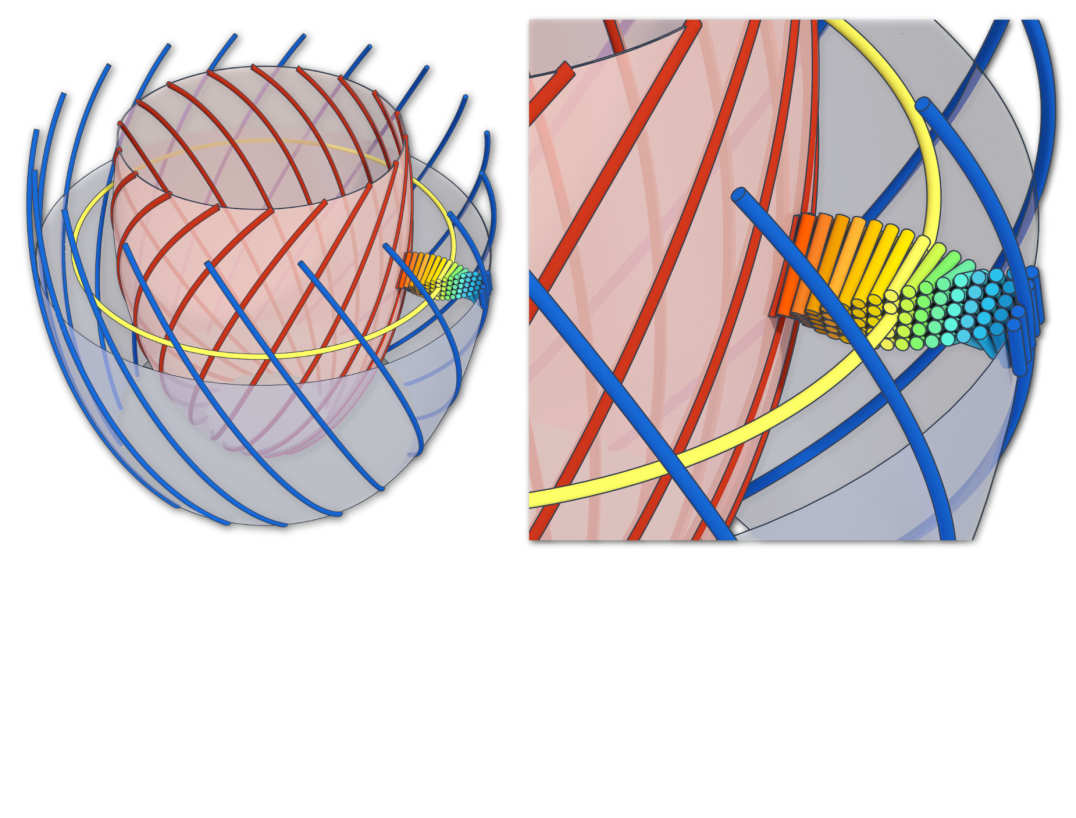
Helical structure of the left ventricle (Nielles-Vallespin S et al. JACC. 2017 Feb 14;69(6):661-676. )
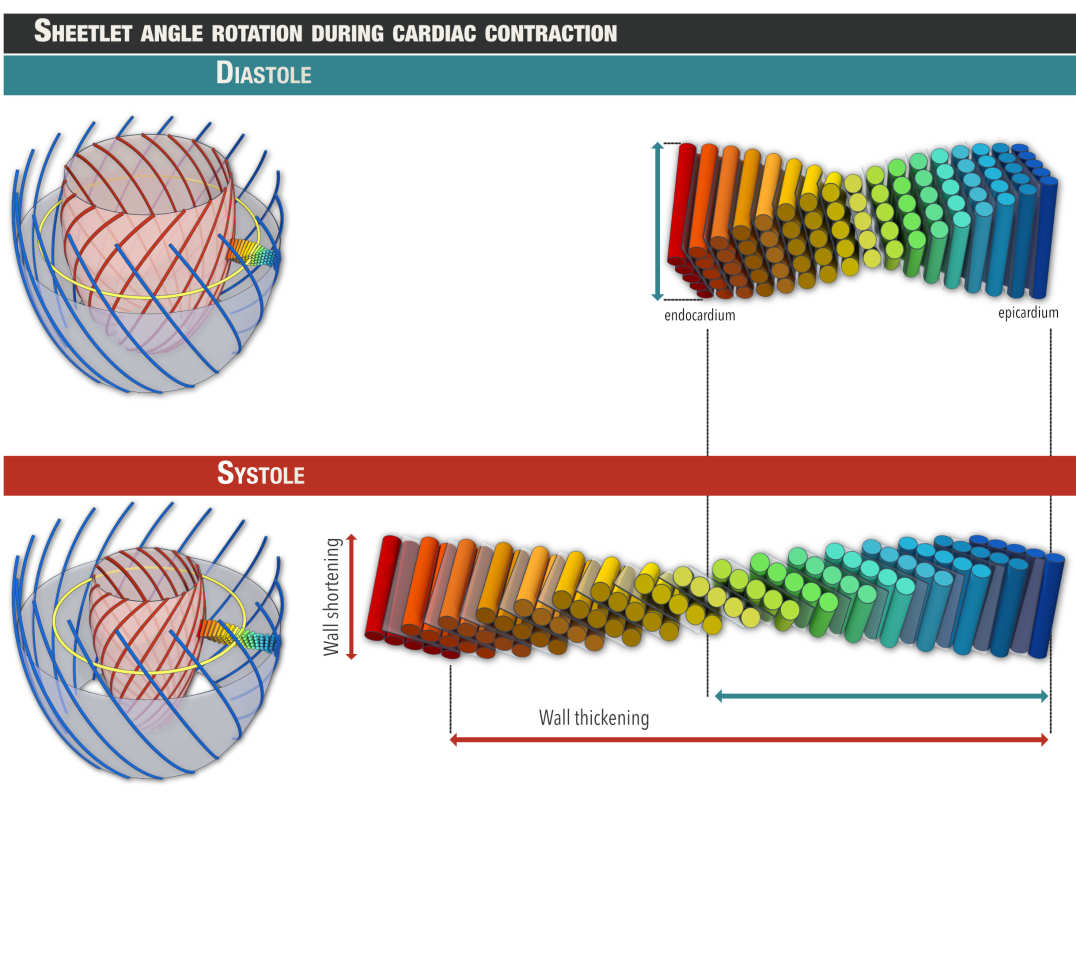
Sheetlet reorientation during cardiac contraction (Nielles-Vallespin S et al. JACC. 2017 Feb 14;69(6):661-676.)
In vivo diffusion tensor cardiac magnetic resonance (DT-CMR) enables non-invasive and non-destructive interrogation of this three-dimensional microstructural organization and its dynamics. DT-CMR quantifies water diffusion in the myocardium, which is constrained by the myocardial micro-architecture. Both in vivo and ex vivo DT-CMR techniques can provide invaluable information about the microstructure of healthy myocardium and the pathophysiological changes in disease.
Research Student Supervision
Lor,C, BSc Medical Biosciences - Optimisation of ex vivo Diffusion Tensor Cardiac Magnetic Resonance and Histology
Tanzer,M, Artificial Intelligence enabled highly efficient Diffusion Tensor Cardiac Magnetic Resonance

