Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Surgery
Our Hamlyn researchers review the recent influential applications of AI in surgery as well as note the major challenges in the future development.
Owing to recent advances in medicine, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has played an important role in supporting clinical decision-making and is now increasingly used for risk stratification, genomics, imaging and diagnosis, precision medicine, and drug discovery.
AI was introduced into surgery more recently, with a strong root in imaging and navigation and early techniques focusing on feature detection and computer-assisted intervention for both pre-operative planning and intra-operative guidance.
That is to say, AI is gradually changing the practice of surgery with technological advancements in imaging, navigation, and robotic intervention.
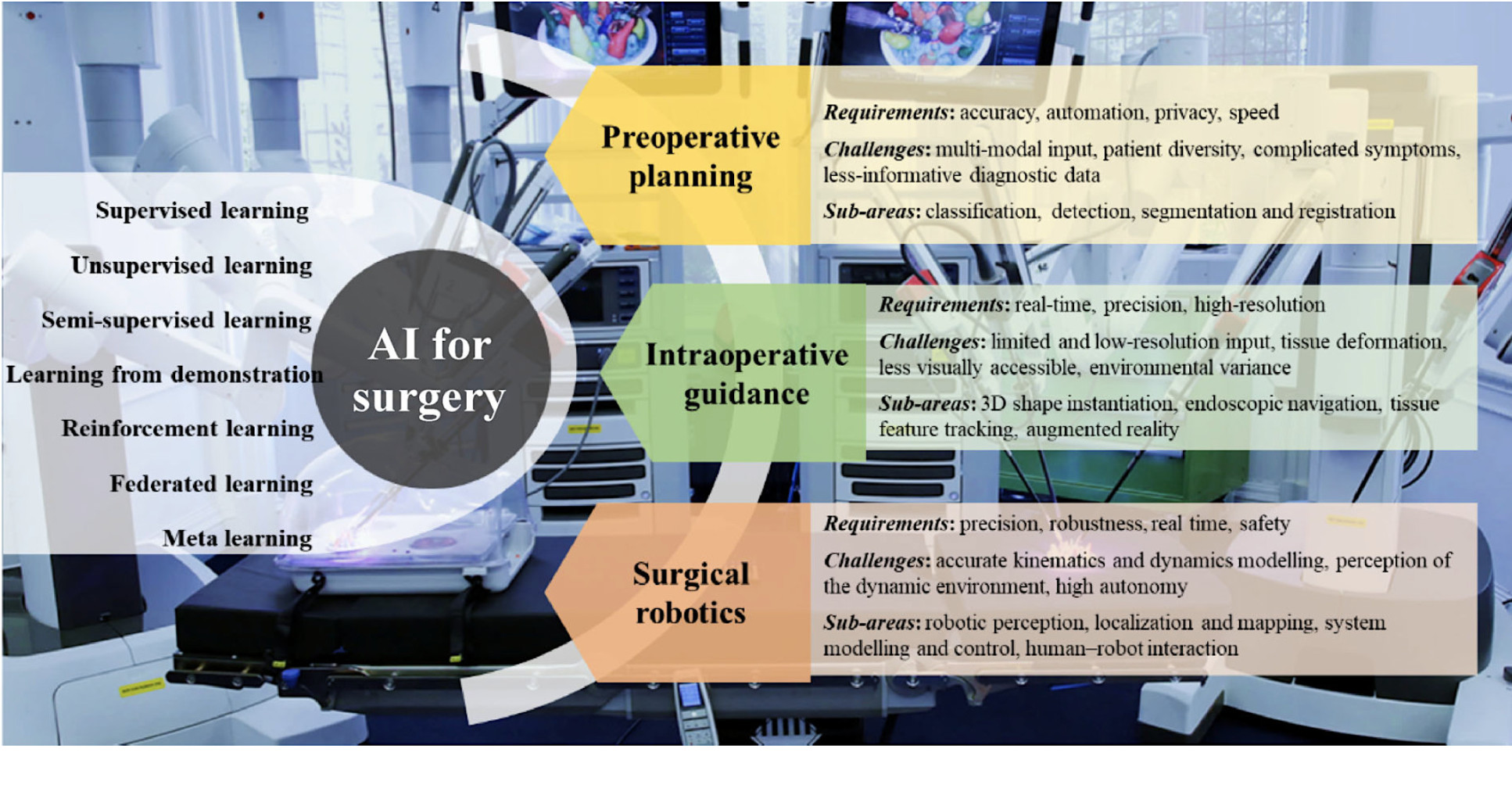
Our researchers at the Hamlyn Centre review the recent successful and influential applications of AI in surgery from pre-operative planning and intra-operative guidance to its integration into surgical robots.
This review paper not only presents an overview of the requirements, challenges and sub-areas of each surgical application segment that applied AI techniques, but also brings attention to the main challenges and provides the potential solutions for the future development of AI in surgery.
AI for preoperative planning
Pre-operative planning where surgeons plan the surgical procedure on the basis of existing medical records and imaging is essential for the success of a surgery.
Our researchers highlighted four routine tasks based on medical imaging that involve AI techniques: (1) anatomical classification, (2) detection, (3) segmentation, and (4) registration.
AI for intraoperative guidance
Surgical trauma is reduced through minimally invasive surgery (MIS), which is now progressively combined with robotic assistance. Computer-aided intra-operative guidance has always been a cornerstone of MIS.
In light of this, learning strategies have been extensively integrated into the development of intra-operative guidance to provide enhanced visualisation and localisation in surgery.
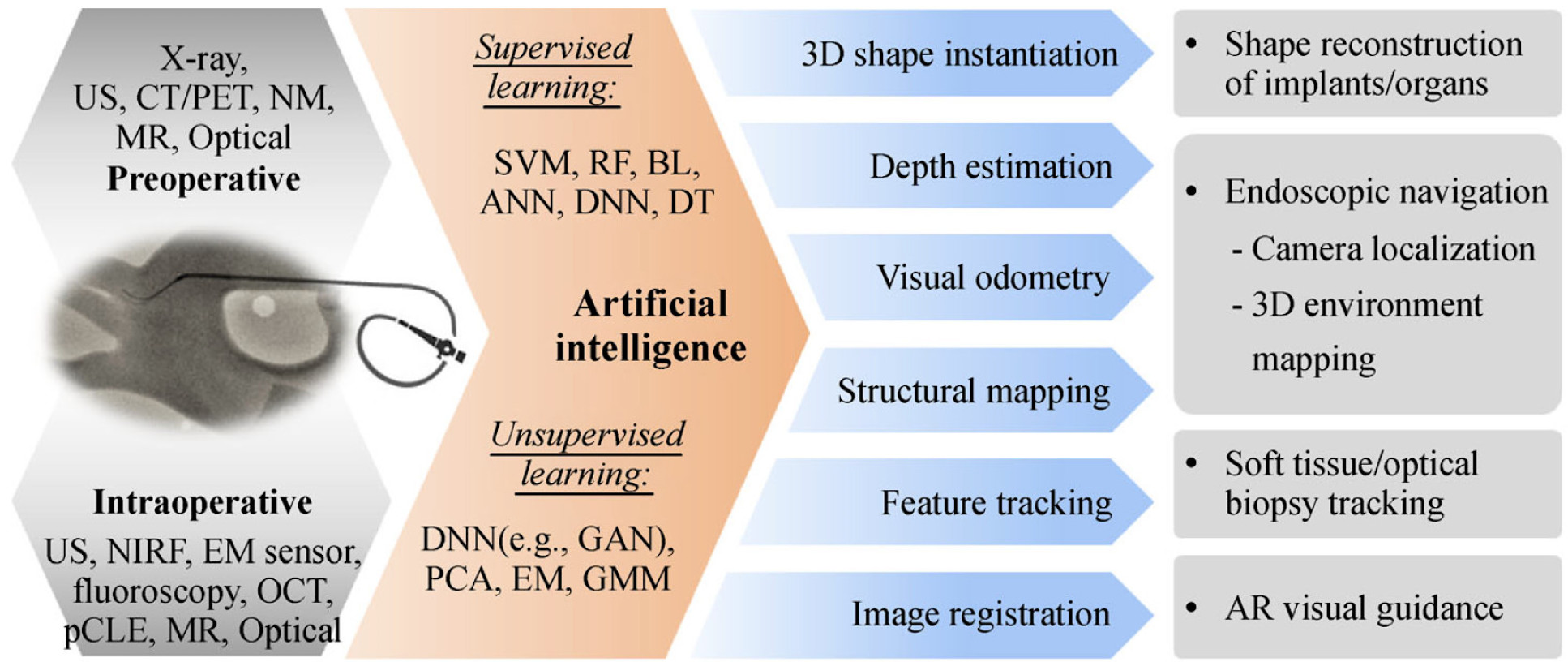
There are four main areas of computer-aided intra-operative guidance in MIS that involve AI techniques: (1) shape instantiation, (2) endoscopic navigation, (3) tissue tracking, and (4) Augmented Reality (AR).
AI for surgical robotics
By virtue of the development of AI techniques, surgical robots can achieve superhuman performance during MIS.
The objective of AI is to boost the capability of surgical robotic systems in perceiving complex in vivo environments, conducting decision-making, and performing the desired tasks with increased precision, safety, and efficiency.
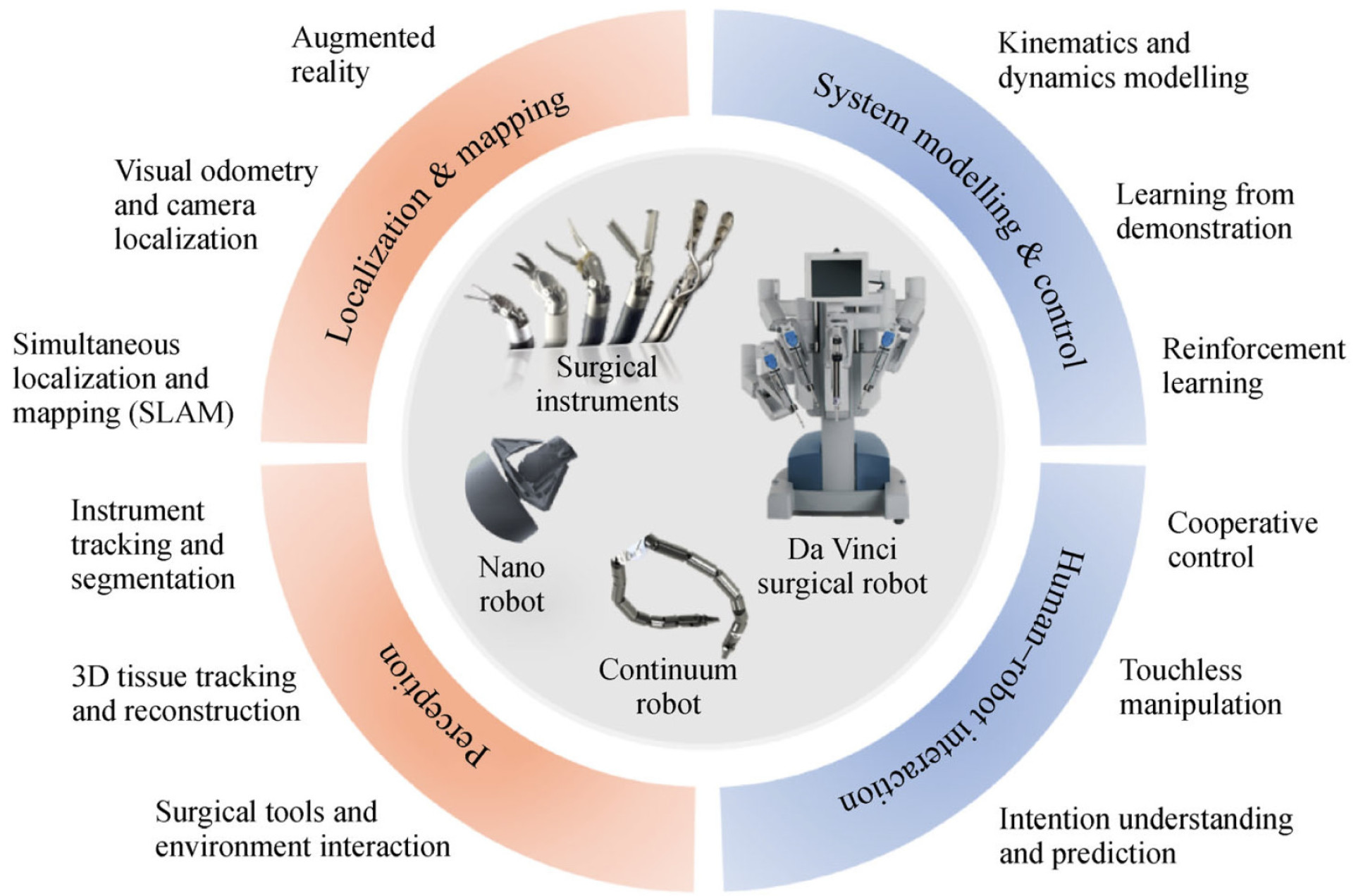
The common AI techniques used for robotic and autonomous systems (RAS) can be summarised in four aspects: (1) perception, (2) localisation and mapping, (3) system modelling and control, and (4) human–robot interaction.
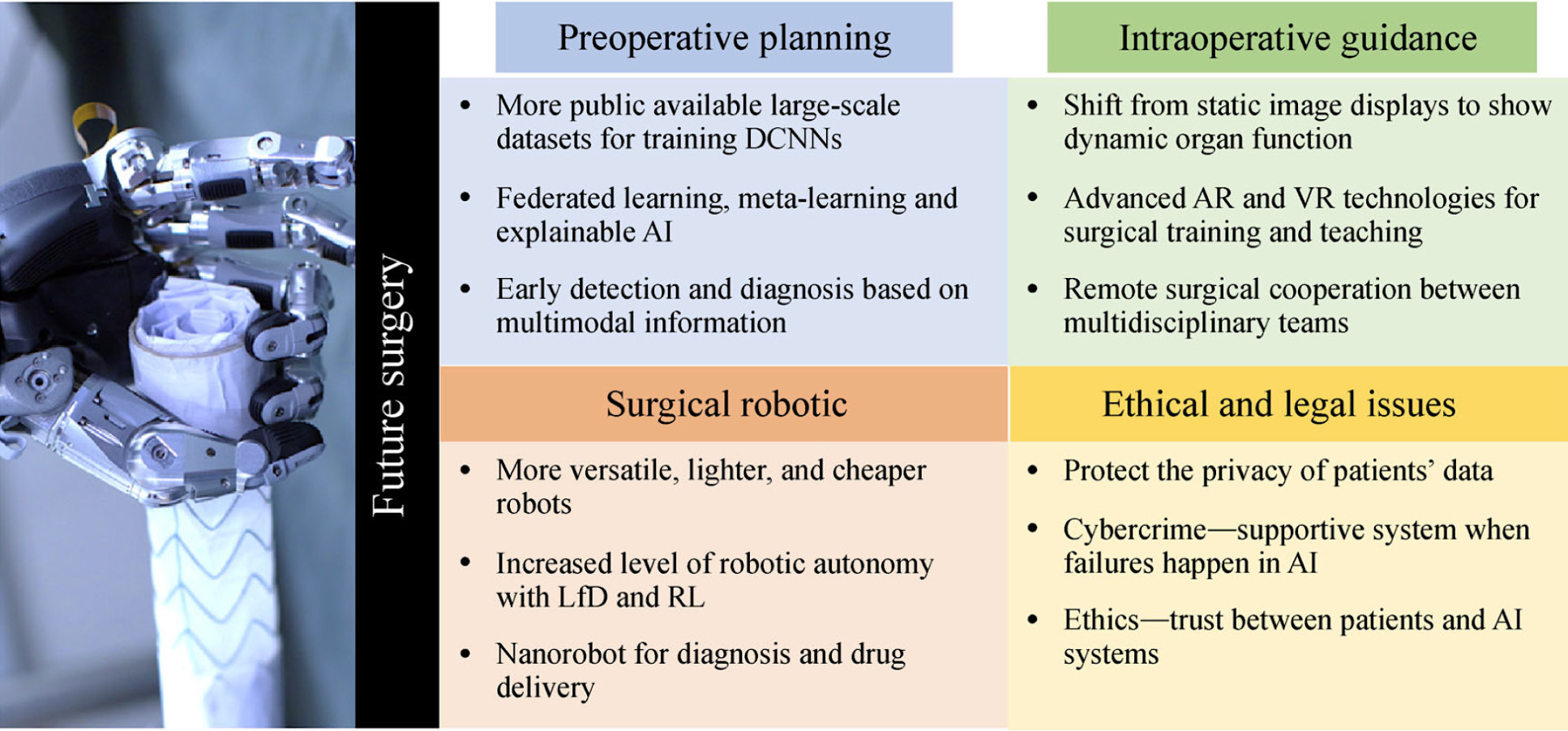
The future development of AI in surgery
The advancement in AI has been transforming modern surgery toward more precise and autonomous intervention for treating both acute and chronic symptoms. By leveraging such techniques, notable progress has been achieved in preoperative planning, intra-operative guidance, and surgical robotics.
In view of this, our researchers summarise the current state, emerging trends, and major challenges in the future development of AI in surgery, as well as provide the potential solutions for overcoming these challenging issues.
Xiao-Yun Zhou, Yao Guo, Mali Shen and , "Application of artificial intelligence in surgery", Frontiers of Medicine, July 2020.
Article supporters
Article text (excluding photos or graphics) © Imperial College London.
Photos and graphics subject to third party copyright used with permission or © Imperial College London.
Reporter
Erh-Ya (Asa) Tsui
Enterprise