The DataLearning Group uses digital twins and data assimilation to model real-world observations, with machine learning used to increase the reliability of predictions made by forecasting models. The group's work has applications including urban air pollution, medical image segmentation, fluid dynamics and wildfire prediction.
DataLearning research topics
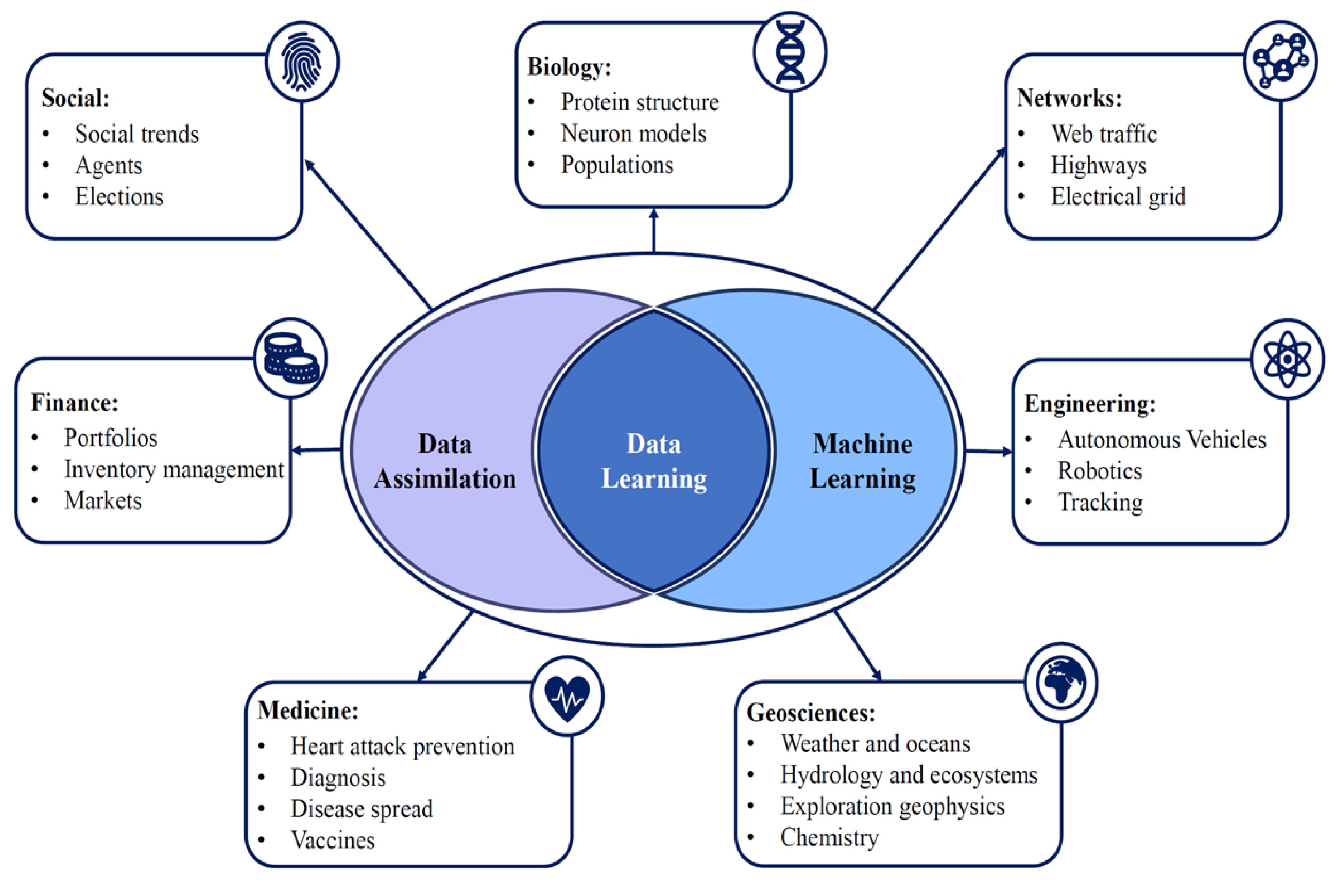
Current research areas
Digital twins
The DataLearning Group develops advanced digital twins; high-fidelity, data-driven virtual representations of real-world systems. These twins serve as intelligent testbeds for scientific inquiry, simulation, and decision support. Core research challenges include ensuring data quality, managing uncertainty, and designing dynamic models that adapt as new information arrives. Increasingly, digital twins are enhanced using AI models and LLMs to support automated reasoning, contextual understanding, and scalable knowledge integration.
Data assimilation
Data assimilation provides a rigorous framework for combining observational data with dynamic physical or computational models. By merging real-time measurements with model predictions, data assimilation techniques estimate the true state of complex systems more accurately. While powerful, classical approaches often rely on idealised assumptions or simplified dynamics. Modern research explores AI-augmented data assimilation, where machine learning and LLM-based reasoning help relax rigid assumptions, improve uncertainty quantification, and adapt models to highly nonlinear environments.
Machine learning
Machine learning (particularly deep learning and foundation AI models) addresses many limitations of traditional modelling. These approaches excel at learning nonlinear behaviours, detecting patterns in high-dimensional data, and generating predictive representations that evolve over time. With the rise of LLMs and multimodal AI models, machine learning now extends to tasks such as natural-language model interrogation, automated feature engineering, and cross-domain knowledge extraction. When integrated with data assimilation, these models produce more resilient, interpretable, and context-aware forecasting tools.
Data learning
Data learning sits at the intersection of data assimilation, machine learning, and modern AI. The DataLearning Group’s approach leverages advanced data-science methodologies (ranging from statistical inference to foundation-model reasoning) to create hybrid systems that adapt to real-world complexity. By unifying physical modelling with data-centric AI, data learning yields flexible, scalable frameworks that enhance predictive accuracy, support real-time decision-making, and enable next-generation intelligent systems.






